July 16, 2014, by Warren Pearce
Evidence-based policy: data has its limits
 This post was originally published on the blog of the Alliance for Useful Evidence, an open–access network of more than 1,800 individuals that champions the use of evidence in social policy and practice.
This post was originally published on the blog of the Alliance for Useful Evidence, an open–access network of more than 1,800 individuals that champions the use of evidence in social policy and practice.
“Aaarghhh! Politics and policy-making is so frustrating! We spend so much time conducting careful scientific analysis in all kinds of fields of enquiry. The results are published in papers subjected to rigorous peer review, then increasingly subjected to extended peer review, then further challenge in the academic literature. This is society’s most robust knowledge. Yet…yet…the politicians just won’t listen. Climate change…badgers…drugs policy…why won’t they listen to us?!”
Definitions: the devil is in the detail
So goes the wailing of many advocates of evidence-based policy (EBP). Support for the concept is apparently widespread. Why wouldn’t it be? It’s fairly hard (though not impossible) to argue against EBP as a general concept. So why is it apparently so hard in practice? One reason is that what we glibly refer to as ‘the evidence’ is not a given: criteria for defining evidence are not necessarily shared between policy participants such as stakeholders, politicians and publics. Neither is policy a fixed object in space and time, such as a regulation, briefing document or target. Rather, it is an ongoing process of understanding between participants. In short, we must be aware of the various meanings of EBP in three particular criteria:
- If ‘evidence’ is policy-useful information, how does knowledge turn into useful information? And how does the context for knowledge-usage affect definitions of evidence?
- Even if a piece of evidence commands widespread support, what are the different meanings it holds for different policy participants?
- What does EBP mean to policy participants as a framework for guiding action? Are some participants powered or disempowered by the demands of EBP?
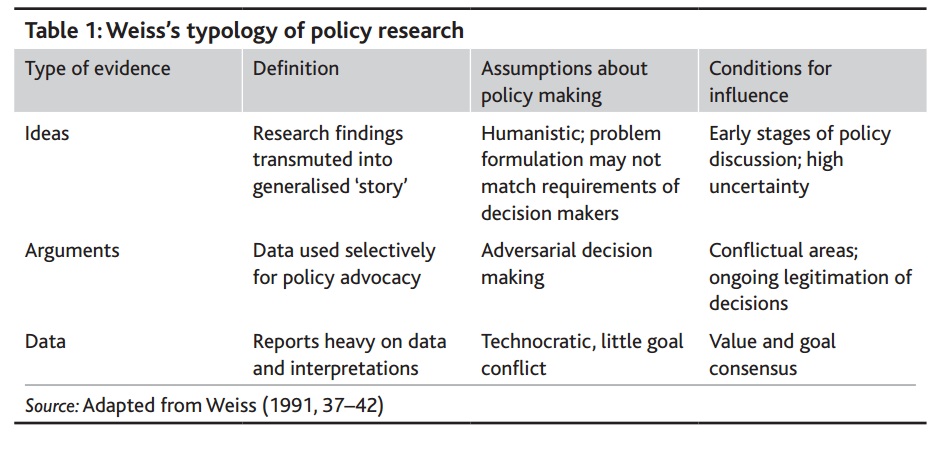
I address some of these questions in a new paper on the implementation of local climate change policy, which uses a typology by Carol Weiss to understand the multiple meanings of ‘evidence’:
The multiple meanings of ‘evidence’
Here, we can see that ‘the evidence’ is not a given, and different assumptions and contexts give rise to the adoption of different forms of evidence. However, other influences come to bear on evidence choices. In particular, the trend for quantitative indicators and targets ushered in by New Labour continues to hold sway in Whitehall and local government. As the old saying goes “the person with the numbers always wins”: if a policy area is to be taken seriously within government, then quantitative benchmarks and targets are a must. Local climate change managers recognised that adopting targets for reducing carbon dioxide emissions was a must if their policy area was to gain credibility, even though they had few policy levers available with which to influence emissions.
To improve policy we need a broader range and style of perspectives
This desire for measurement and comparability across government runs contrary to Weiss’s presentation of evidence as context-specific. Moreover, it has led to misunderstandings of what evidence for policy should be. A turn to data without ideas and arguments leads to the kinds of frustration I caricatured at the beginning of this piece. Responses to climate change, TB in badgers and drug-related health issues can only be properly explained by understanding the functions of different kinds of evidence at different times. And only with these understandings can we hope to improve policy through the utilisation of a broader range and style of perspectives.
FURTHER READING
Warren is the co-editor of a new special issue of ‘Evidence & Policy’ on evidence and meaning in policy making, within which he writes an editorial and a paper on implementing local climate change policy. This post is in part based on the ideas in those two articles.

[…] person (if there is such a thing), other members of the team tackled policy issues, such as the limits of evidence/data-based policy (Warren Pearce), issues around policy in the context of immigration control and the controversial […]